Linux is free.
First ,It's available free of cost (You don't have to pay to use this OS, other OSes like MS-Windows or Commercial version of Unix may cost you money)
Second free means freedom to use Linux, i.e. when you get Linux you will also get source code of Linux, so you can modify OS (Yes OS! Linux OS!!) according to your taste.
It also offers many Software applications, programming languages, and development tools etc. Most of the Program/Software/OS are under GNU General Public License (GPL).
Unix is almost 35 year old Os.
In 1964 OS called MULTICS (Multiplexed Information and Computing
System) was developed by Bell Labs, MIT & General Electric. But this
OS was not the successful one.
Then Ken Thompson (System programmer of Bell Labs) thinks he could do better
(In 1991, Linus Torvalds felt he could do better than Minix
- History repeats itself.). So Ken Thompson wrote OS on PDP - 7 Computer, assembler and few utilities, this is know as Unix
(1969). But this version of Unix is not portable. Then Unix was rewrote in C.
Because
Unix written in 'C', it is portable. It means Unix can run on verity of Hardware
platform (1970-71).
At the same time Unix was started to distribute to Universities. There students and professor started more experiments on Unix. Because of this Unix gain more popularity, also several new features are added to Unix. Then US govt. & military uses Unix for there inter-network (now it is know as INTERNET).
So Unix is Multi-user, Multitasking, Internet-aware Network OS. Linux almost had same Unix Like feature for e.g.
Under GPL the source code is available to anyone who wants it, and can be freely modified, developed, and so forth. There are only a few restrictions on the use of the code. If you make changes to the programs , you have to make those changes available to everyone. This basically means you can't take the Linux source code, make a few changes, and then sell your modified version without making the source code available. For more details, please visit the open-source home page.
| For this Purpose | Use this vi Command Syntax |
| To insert new text | esc + i ( You have to press 'escape' key then 'i') |
| To save file | esc + : + w (Press 'escape' key then 'colon' and finally 'w') |
| To save file with file name (save as) | esc + : + w "filenane" |
| To quit the vi editor | esc + : + q |
| To quit without saving | esc + : + q! |
| To save and quit vi editor | esc + : + wq |
| To search for specified word in forward direction | esc + /word (Press 'escape' key, type /word-to-find) |
| To continue with search | n |
| To search for specified word in backward direction | esc + ?word (Press 'escape' key, type word-to-find) |
| To copy the line where cursor is located | esc + yy |
| To paste the text just deleted or copied at the cursor | esc + p |
| To delete entire line where cursor is located | esc + dd |
| To delete word from cursor position | esc + dw |
| To Find all occurrence of given word and Replace then globally without confirmation | esc +
:$s/word-to-find/word-to-replace/g
For. e.g. :$s/mumbai/pune/g
|
| To Find all occurrence of given word and Replace then globally with confirmation | esc + :$s/word-to-find/word-to-replace/cg |
| To run shell command like ls, cp or date etc within vi | esc + :!shell-command For e.g. :!pwd |
To run script, you need to have in same directory where you created your script, if you are in different directory your script will not run (because of path settings), For
e.g.. Your home directory is ( use $ pwd to see current working directory) /home/vivek.
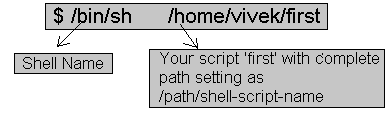
Then you created one script called 'first', after creation of this script you moved to some other directory lets say /home/vivek/Letters/Personal, Now if you try to execute your script it will not run, since script 'first' is in /home/vivek directory, to Overcome this problem there are two ways First, specify complete path of your script when ever you want to run it from other directories like giving following command
$ /bin/sh /home/vivek/first

Now every time you have to give all this detailed as you work in other directory, this take time and you have to remember complete path.
There is another way, if you notice that all of our programs (in form of executable files) are marked as executable and can be directly executed from prompt from any directory. (To see executables of our normal program give command
$ ls -l /bin ) By typing commands like
$ bc
$ cc myprg.c
$ cal
etc, How this happed? All our executables files are installed in directory called /bin and /bin directory is set in your PATH setting, Now when you type name of any command at $ prompt, what shell do is it first look that command in its internal part (called as internal command, which is part of Shell itself, and always available to
execute), if found as internal command shell will execute it, If not found It will look for current directory, if found shell will execute command from current directory, if not found, then Shell will Look PATH setting, and try to find our requested commands executable file in all of the directories mentioned in PATH settings, if found it will execute it, otherwise it will give message
"bash: xxxx :command not found", Still there is one question remain can I run my shell script same as these executables. Yes you can, for this purpose create bin directory in your home directory and then copy your tested version of shell script to this bin directory. After this you can run you script as executable file without using
command like
$ /bin/sh /home/vivek/first
Command to create you own bin directory.
|
$ cd $ mkdir bin $ cp first ~/bin $ first |
Each of above commands Explanation
| Each of above command | Explanation |
| $ cd | Go to your home directory |
| $ mkdir bin | Now created bin directory, to install your own shell script, so that script can be run as independent program or can be accessed from any directory |
| $ cp first ~/bin | copy your script 'first' to your bin directory |
| $ first | Test whether script is running or not (It will run) |
Q.1.How to Define variable x with value 10 and print it on screen.
$ x=10
$ echo $x
Q.2.How to Define variable xn with value Rani and print it on screen
For Ans. Click here
$ xn=Rani
$ echo $xn
Q.3.How to print sum of two numbers, let's say 6 and 3
$ echo 6 + 3
This will print 6 + 3, not the sum 9, To do sum or math operations in shell use
expr, syntax is as follows
Syntax: expr op1 operator op2
Where, op1 and op2 are any Integer Number (Number without decimal point) and operator can be
+ Addition
- Subtraction
/ Division
% Modular, to find remainder For e.g. 20 / 3 = 6 , to find remainder 20 % 3 = 2, (Remember its integer calculation)
\* Multiplication
$ expr 6 + 3
Now It will print sum as 9 , But
$ expr 6+3
will not work because space is required between number and operator (See Shell Arithmetic)
Q.4.How to define two variable x=20, y=5 and then to print division of x and y (i.e. x/y)
For Ans. Click here
$x=20
$ y=5
$ expr x / y
Q.5.Modify above and store division of x and y to variable called z
For Ans. Click here
$ x=20
$ y=5
$ z=`expr x / y`
$ echo $z
Q.6.Point out error if any in following script
| $ vi variscript # # # Script to test MY knolwdge about variables! # myname=Vivek myos = TroubleOS -----> ERROR 1 myno=5 echo "My name is $myname" echo "My os is $myos" echo "My number is myno, can you see this number" ----> ERROR 2 |
ERROR 1 Read this
ERROR 2 Read this
Following script should work now, after corrosponding bug fix!
| $ vi variscript # # # Script to test MY knolwdge about variables! # myname=Vivek myos=TroubleOS myno=5 echo "My name is $myname" echo "My os is $myos" echo "My number is $myno, can you see this number" |
Now consider following command
$($ echo 'expr 6 + 3')
The command ($ echo 'expr 6 + 3') is know as Parameter
substitution. When a command is enclosed in backquotes, the command get
executed and we will get output. Mostly this is used in conjunction with other
commands. For e.g.
| $pwd $cp /mnt/cdrom/lsoft/samba*.rmp `pwd` |
Now suppose we are working in directory called "/home/vivek/soft/artical/linux/lsst" and I want to copy some samba files from "/mnt/cdrom/lsoft" to my current working directory, then my command will be somthing like
$cp /mnt/cdrom/lsoft/samba*.rmp /home/vivek/soft/artical/linux/lsst
Instead of giving above command I can give command as follows
$cp /mnt/cdrom/lsoft/samba*.rmp `pwd`
Here file is copied to your working
directory. See the last Parameter substitution of `pwd` command, expand
it self to /home/vivek/soft/artical/linux/lsst.
This will save my time.
Try to notedown output of following Parameter substitution.
| $echo
"Today date is `date`" $cal > menuchoice.temp.$$ $dialog --backtitle "Linux Shell Tutorial" --title "Calender" --infobox "`cat menuchoice.temp.$$`" 9 25 ; read |
A) There is file called foo, on your disk and you give command, $ ./trmfi foo what will be output.
Ans.: foo file will be deleted, and message "foo file deleted"
on screen will be printed.
B) If bar file not present on your disk and you give command, $ ./trmfi bar what will be output.
Ans.: Message "rm: cannot remove `bar': No such file or
directory" will be printed because bar file does not exist on disk and we
have called rm command, so error from rm commad
C) And if you type $ ./trmfi, What will be output.
Ans.: Following message
will be shown by rm command, because rm is called from script without any
parameters.
rm: too few arguments
Try `rm --help' for more information.
How can I write colorful message on Linux Console? , mostly this kind of question is asked by newcomers (Specially those who are learning shell programming!). As you know in Linux everything is considered as a file, our console is one of such special file. You can write special character sequences to console, which control every aspects of the console like Colors on screen, Bold or Blinking text effects, clearing the screen, showing text boxes etc. For this purpose we have to use special code called escape sequence code. Our Linux console is based on the DEC VT100 serial terminals which support ANSI escape sequence code.
What is special character sequencs and how to write it to Console?
By default what ever you send to console
it is printed as its. For e.g. consider following echo statement,
$ echo "Hello World"
Hello World
Above echo statement prints sequencs of character on screen, but if there
is any special escape sequence (control character) in sequencs , then first some
action is taken according to escape sequence (or control character) and then
normal character is printed on sonsole. For e.g. following echo command prints
message in Blue color on console
$ echo -e "\033[34m Hello Colorful World!"
Hello Colorful World!
Now above echo statement uses ANSI escape sequence (\033[34m), above
entier string ( i.e. "\033[34m Hello Colorful
World!" ) is process as follows
1) First \033, is escape character,
which causes to take some action
2) Here it set screen forground color to Blue using
[34m escape code.
3) Then it prints our normal message Hello Colorful World! in blue
color.
Note that ANSI escape sequence begins with \033 (Octal value) which is represented as ^[ in termcap and terminfo files of terminals and documentation.
You can use echo statement to print
message, to use ANSI escape sequence you must use -e option (switch) with
echo statement, general syntax is as follows
Syntax
echo -e "\033[escape-code
your-message"
In above syntax you have to use\033[
as its with different escape-code
for different operations. As soon
as console recives the message it start to process/read it, and if it found
escape character (\033) it moves to escape mode, then it read "["
character and moves into Command Sequence Introduction (CSI) mode.
In CSI mode console reads a series of ASCII-coded decimal numbers (know as
parameter) which are separated by semicolon (;) . This numbers are read
until console action letter or character is not found (which determines what
action to take). In above example
| \033 | Escape character |
| [ | Start of CSI |
| 34 | 34 is parameter |
| m | m is letter (specifies action) |
Following table show important list of such escape-code/action letter or character
| Character or letter | Use in CSI | Examples |
| h | Set the ANSI mode | echo -e "\033[h" |
| l | Clears the ANSI mode | echo -e "\033[l" |
| m | Useful to show characters in different colors or effects such as BOLD and Blink, see below for parameter taken by m. | echo -e "\033[35m Hello World" |
| q | Turns keyboard num lock, caps lock, scroll lock LED on or off, see below. | echo -e "\033[2q" |
| s | Stores the current cursor x,y position (col , row postion) and attrtributes | echo -e "\033[7s" |
| u | Restores cursor position and attributes | echo -e "\033[8u" |
m understand following paramenters
| Parameter | Meaning | Example |
| 0 | Sets default color schem (White forground and Black background), normal intensity, no blinking etc. | |
| 1 | Set BOLD intensity | $ echo -e "I am
\033[1m BOLD \033[0m Person" I am BOLD Person Prints BOLD word in bold intensity and next ANSI Sequence remove bold effect (\033[0m) |
| 2 | Set dim intensity | $ echo -e "\033[1m BOLD \033[2m DIM \033[0m" |
| 5 | Blink Effect | $ echo -e "\033[5m Flash! \033[0m" |
| 7 | Reverse video effect i.e. Black forground and white background in default color schem | $ echo -e "\033[7m Linux OS! Best OS!! \033[0m" |
| 11 | Shows special control character as graphics character. For e.g. Befor issuing this command press alt key (hold down it) from numric key pad press 178 and leave both key; nothing will be printed. Now give --> command shown in example and try the above, it works. (Hey you must know extended ASCII Character for this!!!) | $ press alt + 178 $ echo -e "\033[11m" $ press alt + 178 $ echo -e "\033[0m" $ press alt + 178 |
| 25 | Removes/disables blink effect | |
| 27 | Removes/disables reverse effect | |
| 30 - 37 | Set forground color 31 - RED 32 - Green xx - Try to find yourself this left as execsise for you :-) |
$ echo -e "\033[31m I am in Red" |
| 40 - 47 | Set background color xx - Try to find yourself this left as execsise for you :-) |
$ echo -e "\033[44m Wow!!!" |
q understand following paramenters
| Parameters | Meaning |
| 0 | Turns off all LEDs on Keyboard |
| 1 | Scroll lock LED on and others off |
| 2 | Num lock LED on and others off |
| 3 | Caps lock LED on and others off |
Click here to see example of q command.
Click here to
see example of m command.
Click here to see example of s and u command.
This is just quick introduction about
Linux Console and what you can do using this Escape sequence. Above table does
not contaies entier CSI sequences. My up-coming tutorial series on C Programming
Language will definatly have entier story with S-Lang and curses (?). What ever
knowledge you gain here will difinatly first step towords the series programming
using c. This much knowledge is sufficient for Shell Programming, now try
the following exersies :-) I am Hungry give me More Programming Excersies
& challeges! :-)
1) Write function box(), that will draw box on screen (In shell
Script)
box (left, top, height, width)
For e.g. box (20,5,7,40)
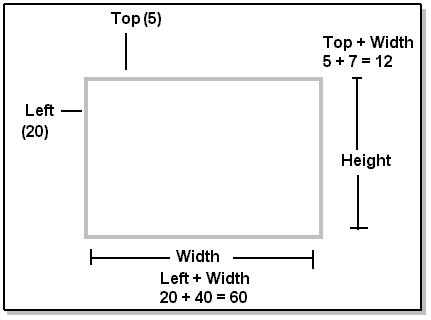
Hint: Use ANSI Escape sequence
1) Use of 11 parameter to m
2) Use following for cursor movement
row;col H
or
rowl;col f
For e.g.
$ echo -e "\033[5;10H Hello"
$ echo -e "\033[6;10f Hi"
In Above example prints Hello message at row 5 and column 6 and Hi at 6th row and 10th Column.
| Shell Built in Variables | Meaning |
| $# | Number of command line arguments. Useful to test no. of command line args in shell script. |
| $* | All arguments to shell |
| $@ | Same as above |
| $- | Option supplied to shell |
| $$ | PID of shell |
| $! | PID of last started background process (started with &) |
See example of $@ and $* variable.
More examples of Shell Script (Exercise for You :-)
First try to write this shell script, as exercise, if any problem or for sample answer to this Shell script open the shell script file supplied with this tutorial.
Q.1. How to write shell script that will add two
nos, which are supplied as command line argument, and if this two nos are not
given show error and its usage
Answer: See Q1 shell Script.
Q.2.Write Script to find out biggest number from
given three nos. Nos are supplies as command line argument. Print
error if sufficient arguments are not supplied.
Answer: See Q2 shell Script.
Q.3.Write script to print nos as 5,4,3,2,1 using
while loop.
Answer: See Q3 shell Script.
Q.4. Write Script, using case statement to
perform basic math operation as
follows
+ addition
- subtraction
x multiplication
/ division
The name of script must be 'q4' which works as follows
$ ./q4 20 / 3, Also check for sufficient command line arguments
Answer: See Q4 shell Script.
Q.5.Write Script to see current date, time,
username, and current directory
Answer: See Q5 shell Script.
Q.6.Write script to print given number in reverse
order, for eg. If no is 123 it must print as 321.
Answer: See Q6 shell Script.
Q.7.Write script to print given numbers sum of
all digit, For eg. If no is 123 it's sum of all digit will be 1+2+3 = 6.
Answer: See Q7 shell Script.
Q.8.How to perform real number (number with
decimal point) calculation in Linux
Answer: Use Linux's bc command
Q.9.How to calculate 5.12 + 2.5 real number calculation at $ prompt in
Shell ?
Answer: Use command as , $ echo 5.12 + 2.5 | bc , here we
are giving echo commands output to bc to calculate the 5.12 + 2.5
Q.10.How to perform real number calculation in shell
script and store result to
third variable , lets say a=5.66, b=8.67, c=a+b?
Answer: See Q10 shell Script.
Q.11.Write script to determine whether given file exist or not, file name
is supplied as command line argument, also check for sufficient number of
command line argument
Answer: See Q11 shell Script.
Q.12.Write script to determine whether given
command line argument ($1) contains "*" symbol or not, if $1 does not
contains "*" symbol add it to $1, otherwise show message "Symbol
is not required". For e.g. If we called this script Q12 then after giving ,
$ Q12 /bin
Here $1 is /bin, it should check whether "*" symbol is present or not
if not it should print Required i.e. /bin/*, and if symbol present then Symbol
is not required must be printed. Test your script as
$ Q12 /bin
$ Q12 /bin/*
Answer: See Q12 shell Script
Q.13. Write script to print contains of file from
given line number to next given number of lines. For e.g. If we called this
script as Q13 and run as
$ Q13 5 5 myf , Here print contains of 'myf' file
from line number 5 to next 5 line of that file.
Answer: See Q13 shell Script
Q.14. Write script to implement getopts statement, your script should
understand following command line argument called this script Q14,
Q14 -c -d -m -e
Where options work as
-c clear the screen
-d show list of files in current working directory
-m start mc (midnight commander shell) , if installed
-e { editor } start this { editor } if installed
Answer: See Q14 shell Script
Q.15. Write script called sayHello, put this script into your startup
file called .bash_profile, the script should run as soon as you logon to system,
and it print any one of the following message in infobox using dialog utility,
if installed in your system, If dialog utility is not installed then use echo
statement to print message : -
Good Morning
Good Afternoon
Good Evening , according to system time.
Answer: See Q15 shell Script
Q.16. How to write script, that will print,
Message "Hello World" , in Bold and Blink effect, and in different
colors like red, brown etc using echo command.
Answer: See Q16 shell Script
Q.17. Write script to implement background
process that will continually print current time in upper right corner of the
screen , while user can do his/her normal job at $ prompt.
Answer: See Q17 shell Script.
Q.18. Write shell script to implement menus using
dialog utility. Menu-items and action according to select menu-item is as
follows
| Menu-Item | Purpose | Action for Menu-Item |
| Date/time | To see current date time | Date and time must be shown using infobox of dialog utility |
| Calendar | To see current calendar | Calendar must be shown using infobox of dialog utility |
| Delete | To delete selected file | First ask user name of directory where all files are present, if no name of directory given assumes current directory, then show all files only of that directory, Files must be shown on screen using menus of dialog utility, let the user select the file, then ask the confirmation to user whether he/she wants to delete selected file, if answer is yes then delete the file , report errors if any while deleting file to user. |
| Exit | To Exit this shell script | Exit/Stops the menu driven program i.e. this script |
Note: Create function for all action for e.g. To show
date/time on screen create function show_datetime().
Answer: See Q18 shell Script.
Q.19. Write shell script to show various system
configuration like
1) Currently logged user and his logname
2) Your current shell
3) Your home directory
4) Your operating system type
5) Your current path setting
6) Your current working directory
7) Show Currently logged number of users
8) About your os and version ,release number , kernel version
9) Show all available shells
10) Show mouse settings
11) Show computer cpu information like processor type, speed etc
12) Show memory information
13) Show hard disk information like size of hard-disk, cache memory, model etc
14) File system (Mounted)
Answer: See Q19 shell Script.